Membrane information
Not every membrane and solvent interacts effectively. This brief guide will help you select the most appropriate membrane for your application by considering chemical compatibility.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Hydrophobic membrane. Resistant to organic solvents as well as strong acids and bases. Low protein
binding. Low in extractables. Main applications are the filtration of non-aqueous samples. Prior to
filtering of aqueous samples the membrane must be pre-wetted with a water-miscible organic solvent.
Polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF)
Hydrophilic membrane. Resistant to a broad range of organic solvents. Low protein binding.
Polypropylene (PP)
Slightly hydrophobic membrane. Resistant to a wide range of organic solvents.
Polyethersulfone (PES)
Hydrophilic membrane. Broad solvent compatibility. Suitable for filtration of aqueous and compatible
organic solvents. Higher liquid flow than either PTFE or PVDF. Low in extractables. Low protein binding.
Nylon/polyamide (NYL)
Hydrophilic membrane. Resistant to a range of organic solvents. Suitable for use with high pH samples.
Binds proteins, which makes it unsuitable for protein recovery applications.
Cellulose acetate (CA)
Hydrophilic membrane. Limited solvent resistance. Very low protein binding capacity, which makes it
an excellent choice for protein recovery applications.
Cellulose nitrate (CN)
Hydrophilic membrane. Limited resistance to organic solvents. High liquid flow rate. High protein
binding capacity, which makes it unsuitable for protein recovery applications.
Regenerated cellulose (RC)
Hydrophilic membrane. Resistant to a very wide range of solvents. Suitable for use with either aqueous
solutions or organic solvents. Compatible with HPLC solvents. Very low protein binding capacity, which
makes it an excellent choice for protein recovery applications.
Anopore (ANP) (membrane used in Anotop™ filters)
Anopore™ is a hydrophilic membrane with excellent organic solvent compatibility. Suitable for use with
both aqueous and organic samples. The membrane has very tight pore-size distribution. Not suitable
for use with very acidic or very basic samples.
Glass microfiber/glass fiber (GMF/GF)
Hydrophilic material. Excellent compatibility with organic solvents and strong acids (apart from
hydrofluoric acid) and bases. Either used as a prefilter or as a final filter.
Chemical compatibility of membranes and housings
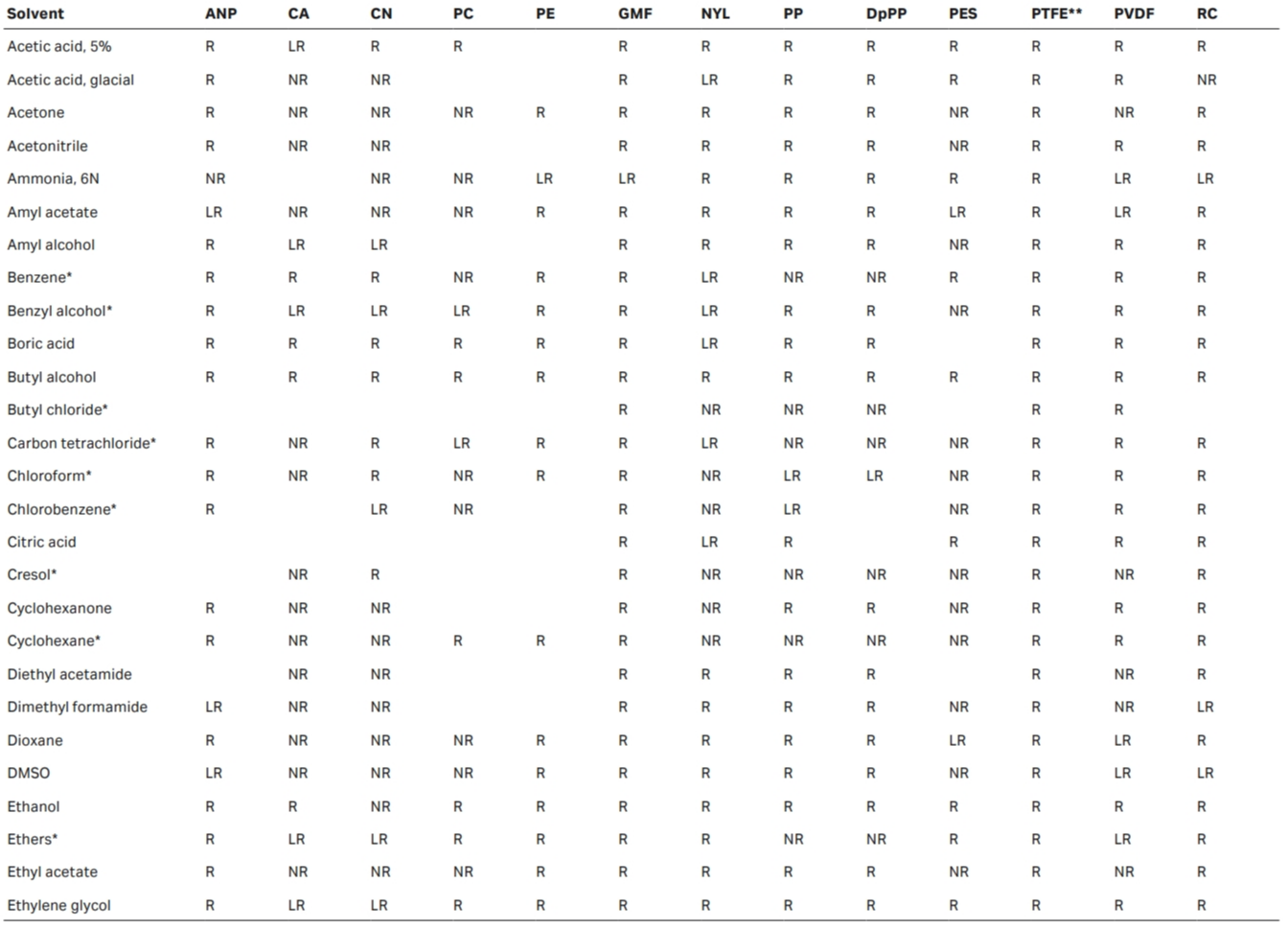
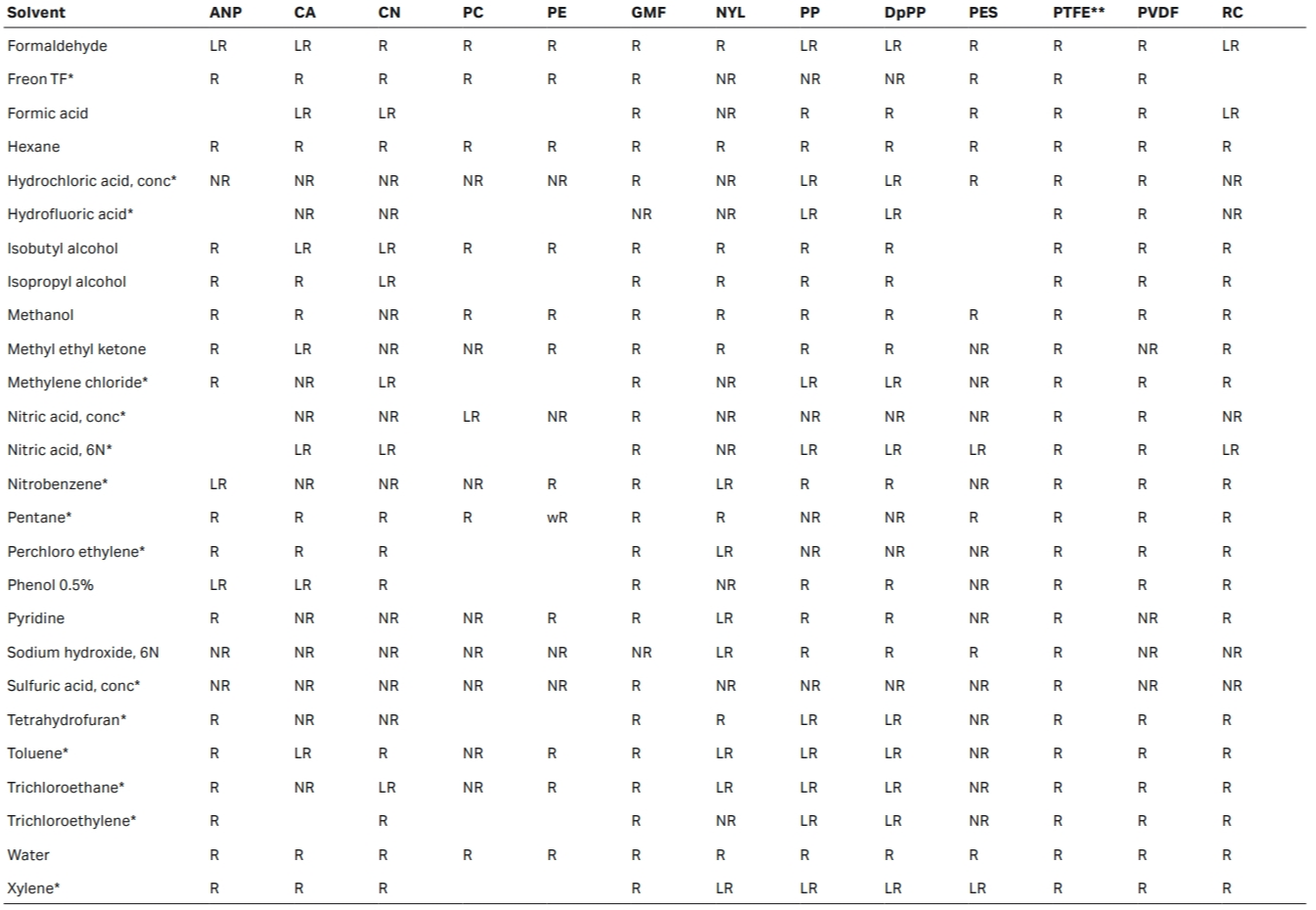
R = Resistant; LR = Limited Resistance; NR = Not Recommended
* Short-term resistance of housing
The above data is to be used as a guide only. Testing prior to application is recommended.
** Membrane may need pre-wetting with isopropanol/methanol if filtering a polar liquid
Material abbreviations:
ANP — Anopore
CA — Cellulose Acetate
CN — Cellulose Nitrate
DpPP — Polypropylene Depth Filter
GMF — Glass Microfiber
NYL — Nylon
PC — Polycarbonate
PE — Polyester
PES — Polyethersulfone
PP — Polypropylene
PTFE — Polytetrafluoroethylene
PVDF — Polyvinylidene Difluoride
RC — Regenerated Cellulose